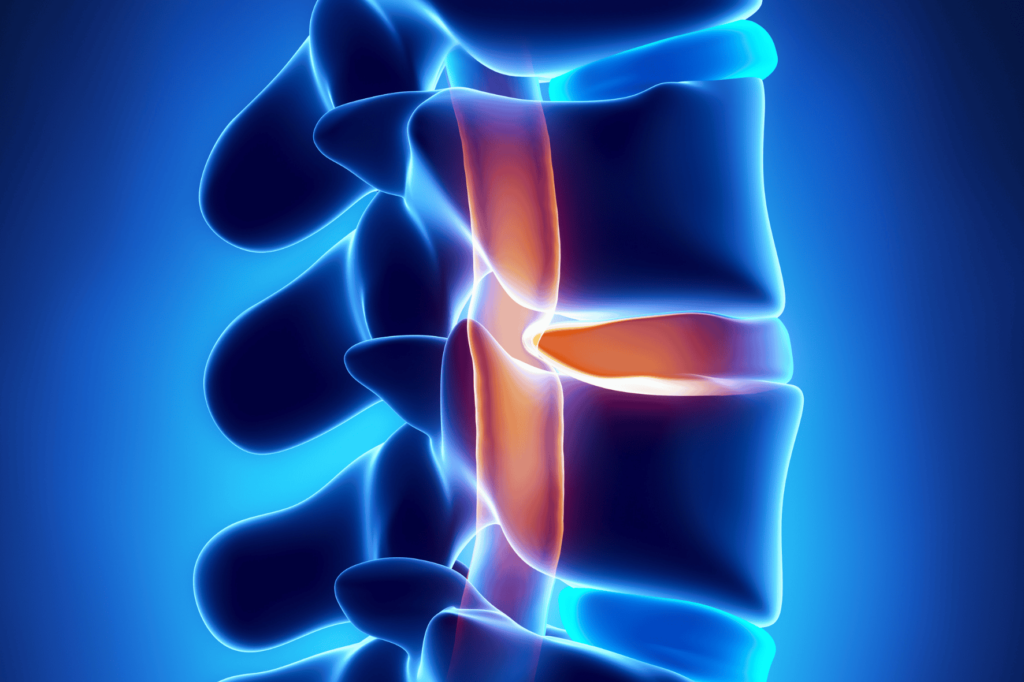
Understanding Herniated Discs and Treatment Options
Herniated discs, also known as slipped or ruptured discs, occur when the inner gel-like core of a spinal disc leaks out through a tear in the outer layer. This condition can cause significant pain, numbness, and weakness, primarily in the back, legs, or arms, depending on the location of the affected disc. Herniated discs often result from aging, injury, or strain, with repetitive motions, improper lifting techniques, and trauma contributing to the condition. Symptoms typically include back pain, leg or arm pain, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness, diagnosed through physical examinations and imaging tests like MRI or CT scans.
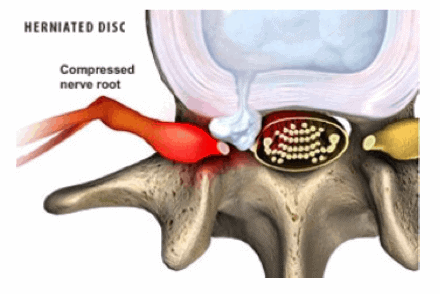
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense for herniated discs, aiming to relieve pain and improve function. Physical therapy focuses on strengthening the muscles around the spine, improving flexibility, and reducing pain through targeted exercises. Over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and corticosteroid injections can help manage pain and inflammation. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and avoiding activities that strain the back can prevent the condition from worsening.
When non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief, surgical options may be considered to alleviate symptoms and restore function. Surgery is recommended for patients with severe pain, significant weakness, or loss of bladder or bowel control that does not improve with conservative treatments. The primary goals of surgery are to relieve pressure on the affected nerves, reduce pain, and improve mobility and function.
Microdiscectomy
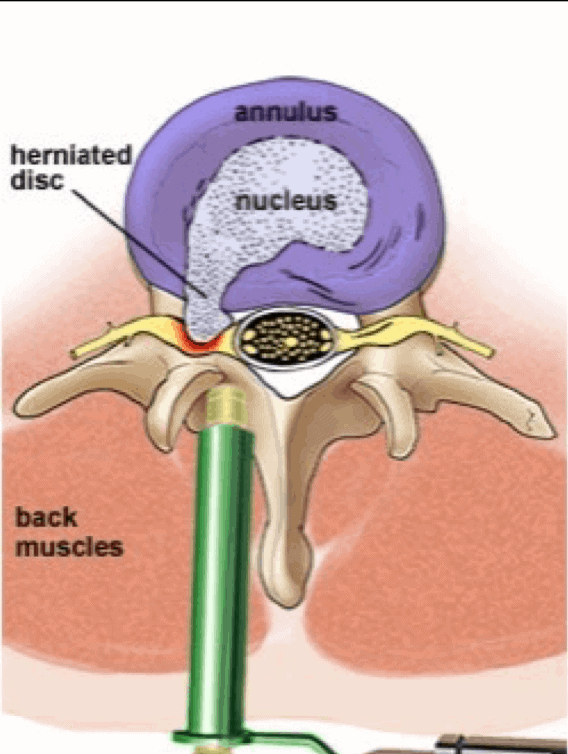
Microdiscectomy is a common surgical procedure used to treat herniated discs by removing the portion of the disc that is pressing on a nerve. This minimally invasive procedure involves making a small incision in the back, through which the surgeon uses a microscope to remove the herniated portion of the disc while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. Microdiscectomy can provide quick pain relief, has a high success rate, and allows for a relatively short recovery period. However, possible risks include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and recurrence of the herniation.
Laser Endoscopic Spine Surgery
Laser endoscopic spine surgery (LESS) is a newer, minimally invasive technique that uses a laser and endoscope to treat herniated discs. During this procedure, a small 1 cm incision is made, and an endoscope is inserted to visualize the affected area. A non-electrical laser is then used to safely treat the herniation. This tiny incision is covered with a band-aid, and most patients walk within an hour of surgery, go home the same day, and return to work within 1-2 weeks. Benefits of laser endoscopic spine surgery include minimal tissue damage, no bone resection, no tendon detachment, and a quicker recovery time. As with any surgery, risks include infection, bleeding, and nerve damage, but these are minimized due to the minimally invasive nature of the procedure.
Choosing the right surgical option depends on various factors, including the patient’s specific condition and overall health. Both microdiscectomy and laser endoscopic spine surgery are effective in relieving pain and improving function. Microdiscectomy is well-established with a high success rate, while laser endoscopic surgery offers a less invasive alternative with similar outcomes and generally faster recovery times. Microdiscectomy is suitable for most patients with herniated discs, while laser endoscopic surgery is ideal for those seeking a minimally invasive option with a quicker recovery.
In conclusion, herniated discs can cause significant pain and require appropriate treatment. Non-surgical options such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes are often effective. When surgery is necessary, both microdiscectomy and laser endoscopic spine surgery offer effective solutions. Consulting with a specialized spine surgeon, such as those at Excel Spine, can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Click here for a short video on herniated disc surgery options.
FAQ’s
What is the recovery time for a microdiscectomy? Recovery time for a microdiscectomy typically ranges from 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the patient’s overall health and adherence to post-surgical guidelines.
How do I know if I need surgery for my herniated disc? Surgery is considered if non-surgical treatments fail to relieve symptoms, or if there is significant pain, weakness, or loss of bladder or bowel control.
What are the advantages of minimally invasive spine surgery? Minimally invasive spine surgery, such as laser endoscopic surgery, typically results in less pain, shorter recovery times, and minimal scarring.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent herniated discs? Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and avoiding activities that strain the back can help prevent herniated discs.
How does a herniated disc differ from a bulging disc? A bulging disc occurs when the disc protrudes out of its normal space but remains intact, while a herniated disc involves a tear in the outer layer, allowing the inner gel to leak out.
What activities should I avoid if I have a herniated disc? Avoid heavy lifting, repetitive bending or twisting, high-impact activities, and sitting or standing for long periods without breaks.
Can herniated discs heal on their own? In some cases, herniated discs can heal with time and non-surgical treatments. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, medical intervention may be necessary.
What is the success rate of microdiscectomy surgery? Microdiscectomy surgery has a high success rate, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief and improved function.
Is laser endoscopic spine surgery covered by insurance? Coverage for laser endoscopic spine surgery varies by insurance provider. It’s essential to check with your insurance company to determine coverage and any potential out-of-pocket costs.
How soon can I return to normal activities after laser endoscopic spine surgery? Most patients can return to normal activities within 1-2 weeks after laser endoscopic spine surgery, although this can vary depending on individual recovery rates and adherence to post-operative guidelines.
Are there any dietary recommendations for patients with herniated discs? A healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can help reduce inflammation and support overall spine health.
What role does genetics play in herniated discs? Genetics can play a role in the susceptibility to herniated discs, with certain inherited traits potentially making some individuals more prone to disc degeneration.
Can herniated discs cause permanent nerve damage? If left untreated, severe herniated discs can cause permanent nerve damage. Timely medical intervention is crucial to prevent long-term complications.
What is the role of physical therapy in recovery from herniated disc surgery? Physical therapy is essential in recovery, helping to strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and promote proper body mechanics to prevent future injuries.
